Research
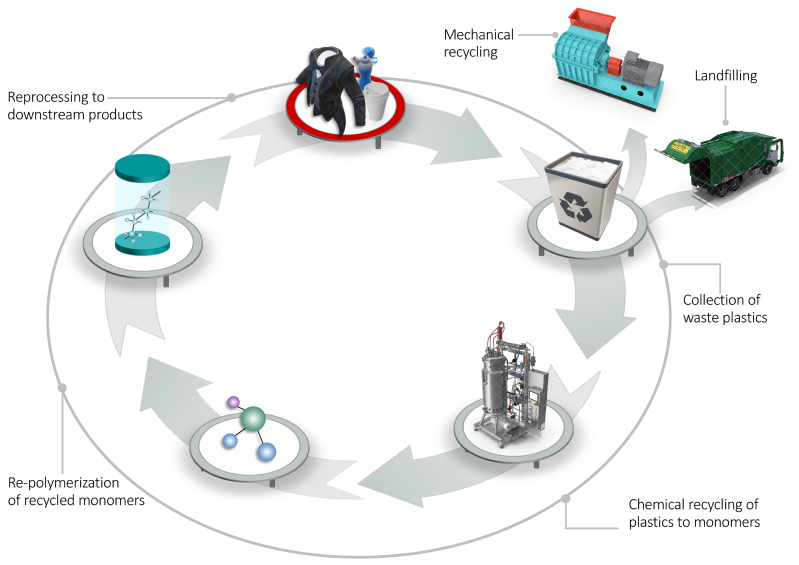
*Chemical Upcycling of Plastics*
Plastics help build our modern society. Despite these benefits, the use of plastics is causing imminent environmental disasters due to the long service life of plastics and the lack of effective end-of-life options. Currently, only 15% of waste plastics enter the recycling route, and landfills account for 65% of scrap options. Efficient recycling of waste plastics not only contributes to sustainable environmental development, but also has important economic benefits and reduces energy consumption.Plastic recycling can be divided into four levels. Primary recycling refers to the reprocessing of waste plastics into plastics for the same purpose. Secondary (mechanical) recycling is the use of recycled plastic for other products. The products obtained are usually of lower value, so the process is often referred to as down-cycling. It is worth noting that both of these recycling methods rely heavily on thermomechanical methods, which has the problem of contaminations-accumulation in downstream products. In addition, thermal processing causes the break of the molecular chain, thereby reducing the thermal and mechanical strength. Tertiary (chemical) recycling refers to the degradation of polymer molecules into corresponding monomer analogs, which can be used to make new plastics and/or raw materials for other materials. Another method of recycling waste plastics is incineration, which can recover part of the energy in plastics. But its carbon emissions are very large, and it does not allow the recycling of original components. The chemical recycling is sustainable and is expected to achieve upcycling.
Chemical recycling is the broad term used to describe a range of emerging technologies in the waste management industry which allow plastics to be recycled, that are difficult or uneconomic to recycle mechanically. By turning plastic waste back into base chemicals and chemical feedstocks, chemical recycling processes have the potential to dramatically improve recycling rates and divert plastic waste from landfill or incineration. Chemical recycling complements mechanical recycling processes by enabling the further extraction of value from polymers that have exhausted their economic potential for mechanical processing. Chemical recycling serves as an alternative to landfill and incineration for erstwhile hard-to-recycle plastic products such as films, multi-layered and laminated plastics. Additionally, chemical recycling supplies virgin-quality raw materials to the plastics supply chain. This enables the production of food grade plastics from post-consumer waste.
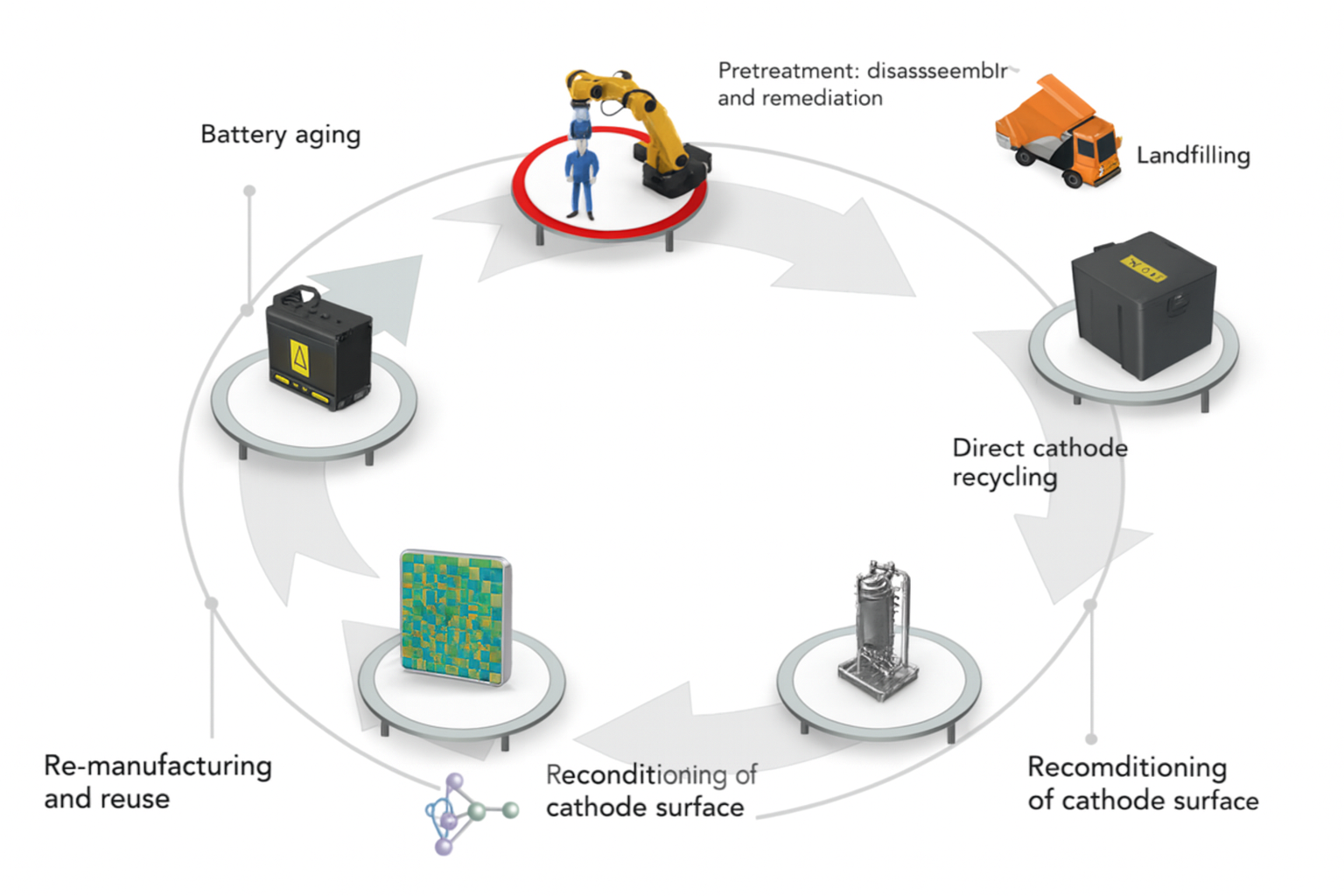
*Spent Lithium-ion Batteries Upcycling*
Direct recycling methodologies focus on regenerating functional battery components without breaking down their core chemical structures. Current efforts primarily center on reviving spent cathode materials. This stands in contrast to conventional pyrometallurgical or hydrometallurgical processes, which decompose cathode compounds into raw metals. Through relithiation and controlled thermal annealing, the degraded cathode structure can be repaired, restoring its electrochemical performance for reuse in new batteries—effectively achieving upcycling. Simultaneously, processes are being developed to recover and purify other components such as anodes and electrolytes. Still, wider adoption of direct recycling faces several hurdles, including complexities in separating different battery materials and sensitivity to the initial degradation level of the cells. By renewing the intrinsic value of electrode materials with relatively low energy input and minimal chemical waste, this approach represents a promising route toward establishing a circular economy for the battery industry.
